
BfR Recommendation XXXVI
Food contact compliance of paper and board materials
- Recommendation valid for single and multi-layered commodities (articles, materials) made of paper or paperboard which are intended to come into contact with or affect foodstuffs
- Positive lists of authorised substances
General informations
The recommendations drawn up by the BfR (Ger-man Federal Institute for Risk Assessment) are in line with European Framework Regulation (EC) no. 1935/2004 and concern materials intended for food contact. Unlike French Information Note from DGC-CRF – Fiche MCDA N°4 (January 1st 2019) issued by the French General Directorate for Competition Policy, Consumer Affairs and Fraud Control (DGC-CRF), the BfR’s documents draw up a positive list of authorised substances for manufacturing single or multilayer paper and board-based products or objects.
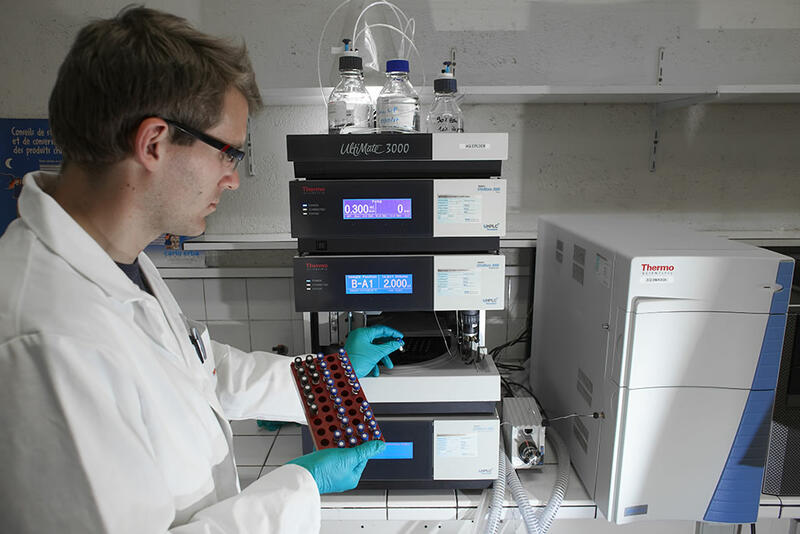
The three laboratories that form the Food Contact unit at the CTP are equipped to perform chemical, microbiological and sensory analyses, and aim to provide comprehensive and independent expertise.
The CTP can also organise training courses on the theme of food contact, provide technical assistan-ce and advise on Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP).
Technical data and achievements
Various recommendations
The BfR’s Recommendations are broken down into four reference documents, depending on how the finished pro-duct will be used:
- BfR XXXVI: for food contact at temperatures up to 90°C
- BfR XXXVI/1: for Cooking Papers, Hot Filter Papers and Filter Layers, contact with aqueous foodstuffs only
- BfR XXXVI/2: for Paper and Paperboard for Baking Purposes (up to 220°C)
- BfR XXXVI/3: for Absorber pads based on cellulosic fibres for food packaging
Mandatory analyses
The analyses that must be carried out to comply with the BfR recommendations can vary among those on the following list, depending on the type of foodstuff with which the material will come into contact (dry and non-fatty, aqueous and/or fatty):
- Transfer of antimicrobial constituents (EN 1104)
- Assessment of off-flavour transmitted (EN 1230-2)
- Evaluation of odour (EN 1230-1)
- Determination of colour fastness (EN 646)
- Fastness of fluorescent whitened paper and board (EN 648)
- Lead and cadmium in aqueous extracts (NF EN 12498)
- Quantitative analysis of aluminium using inductively coupled plasma (ICP) spectrometry
Case of recycled fibres
In addition to the aforementioned situations, other specific analyses are carried out when recycled fibres are included in the composition :
- Quantitative analysis of phthalates DEHP, DIBP and DBP
- Quantitative analysis of benzophenone
- Quantitative analysis of diisopropylnaphthalene (DIPNs)
- Quantitative analysis of Michler’s ketone, also referred to as 4,4’-Bis(dimethylamino)-benzophenone
- Quantitative analysis of bisphenol A (BPA)
- Quantitative analysis of bisphenol S (BPS)
- Migration of hydrophobic and volatile substances
Restricted Substances
The CTP’s experts use the data contained in composition sheets, declarations of conformity or other documents issued by suppliers to identify the presence of restricted substances. When necessary they arrange appropriate analyses for each component present in glues, adhesives, inks, optical brighteners or dyes such as formaldehyde, epichlorohydrin, glyoxal, CMIT/MIT/BIT, 3-MCPD, DCP, AKD, Bronopol, etc. To facilitate relations between clients and suppliers and the gathering of this information, the CTP can also act as a third party and draw up non-disclosure agreements without un-dermining guarantees of consumer safety.
 |
 |
|
| Liquid chromatography analysis – Mass spectrometry |
Symbol guaranteeing food contact suitability |